Californium(III) iodide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Californium triiodide[1]
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CfI3 | |
| Molar mass | 632 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | red-orange solid |
| Density | g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 800 °C (1,470 °F; 1,070 K) |
| insoluble | |
| Structure | |
| trigonal | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Einsteinium(III) iodide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Californium(III) iodide is a binary inorganic compound of californium and iodine with the formula CfI
3.[2][3]
Synthesis[edit]
Californium triiodide can be prepared in microgram quantities under high vacuum. It can be prepared at 500 °C from californium(III) hydroxide and hydrogen iodide:
- Cf(OH)3 + 3HI → CfI3 + 3H2O
Physical properties[edit]
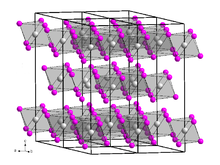
The compound forms a red-orange solid. The triiodide sublimes at ~800 °C without melting. It crystallizes in the trigonal crystal structure in the space group R3 (No. 148) with the lattice parameters a = 758.7 pm and c = 2081.4 pm with six formula units per unit cell. Its crystal structure is isotypic with that of bismuth(III) iodide.
References[edit]
- ^ "WebElements Periodic Table » Californium » californium triiodide". webelements.com. Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- ^ Macintyre, Jane E. (23 July 1992). Dictionary of Inorganic Compounds. CRC Press. p. 2826. ISBN 978-0-412-30120-9. Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- ^ ERDA Energy Research Abstracts. ERDA Technical Information Center, etc.; Washington. 1977. p. 565. Retrieved 11 April 2023.
