User:Mr. Ibrahem/Lofexidine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Britlofex, Lucemyra, Kai Er Ding, others |
| Other names | Lofexidine hydrochloride |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablets) |
| Drug class | α2 adrenergic receptor agonist[1] |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | >90% |
| Protein binding | 80–90% |
| Metabolism | Liver (glucuronidation) |
| Elimination half-life | 11 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
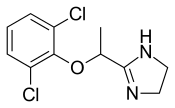
| Formula | C11H12Cl2N2O |
| Molar mass | 259.13 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| | |
Lofexidine, sold under the brand name Lucemyra among others, is a medication used to treat opioid withdrawal.[2] It is not as effective as buprenorphine.[3] It is taken by mouth.[1] It may be used for up to two weeks and should be stopped gradually.[3][2]
Common side effects include trouble sleeping, low blood pressure with standing, slow heart rate, sleepiness, and dry mouth.[1] Other side effects may include QT prolongation.[1] Use in pregnancy is of unclear safety.[1] It is an α2 adrenergic receptor agonist.[1]
Lofexidine was approved for use medical use in the United States in 2018.[1] In the United States 84 tablets of 0.18 mg costs about 1,700 USD as of 2021.[4] The similar medication clonidine costs less than 10 USD.[3] It is not commercially available in the United Kingdom as of 2021.[2]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Lofexidine Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 18 January 2021. Retrieved 24 November 2021.
- ^ a b c d BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 526. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- ^ a b c Bryce, Carl (15 March 2019). "Lofexidine (Lucemyra) for Treatment of Opioid Withdrawal Symptoms". American Family Physician. 99 (6): 392–394. ISSN 0002-838X. Archived from the original on 5 March 2021. Retrieved 24 November 2021.
- ^ "Lucemyra Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Retrieved 24 November 2021.
