User:Mr. Ibrahem/Desloratadine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Aerius, Allex, Clarinex, others[1][2] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a602002 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablets, solution) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Rapidly absorbed |
| Protein binding | 83 to 87% |
| Metabolism | UGT2B10, CYP2C8 |
| Metabolites | 3-Hydroxydesloratadine |
| Onset of action | Within 1 hour[3] |
| Elimination half-life | 27 hours |
| Duration of action | Up to 24 hours[3] |
| Excretion | 40% as conjugated metabolites into urine Similar amount into the feces |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
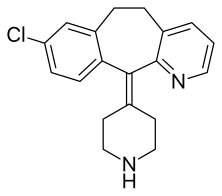
| Formula | C19H19ClN2 |
| Molar mass | 310.83 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Desloratadine, sold under the brand name Clarinex among others, is a medication used to treat allergies such as hay fever and hives.[3] Onset occurs within an hour and lasts for up to 24 hours.[3] It is taken by mouth.[3]
Common side effects include nausea, tiredness, dry mouth, and headache.[3] A lower dose is recommended in those with kidney or liver problems.[3] While there is no clear evidence of harm during pregnancy, such use is generally not recommended.[4][5] It is a second generation antihistamine.[3] It is an active metabolite of loratadine.[3]
Desloratadine was patented in 1984 and came into medical use in 2001.[6] In the United Kingdom it is avaliable as a generic medication and costs the NHS about 1.5 pounds per month.[4] In the United States this amount costs about 17 USD.[7] It is also available with pseudoephedrine.[3]
References[edit]
- ^ Murdoch, David; Goa, Karen L.; Keam, Susan J. (April 7, 2003). "Desloratadine: an update of its efficacy in the management of allergic disorders". Drugs. 63 (19): 2051–2077. doi:10.2165/00003495-200363190-00010. PMID 12962522.
- ^ "Allex EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Archived from the original on 2020-12-27. Retrieved 2020-04-05.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Desloratadine Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 2020-08-12. Retrieved 2021-07-16.
- ^ a b BNF (80 ed.). BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. September 2020 – March 2021. p. 294. ISBN 978-0-85711-369-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date format (link) - ^ "Desloratadine Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 549. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 2020-12-27. Retrieved 2020-05-09.
- ^ "Desloratadine Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Archived from the original on 10 September 2016. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
