User:Dak/aids2
NOTE: THIS ISN'T WIKIPEDIAS ARTICLE ON AIDS, THIS IS A TEMPORARY WORKING COPY FOR ME. FOR WIKIPEDIA'S ARTICLE, CLICK HERE --> AIDS
TODO:
dump article under below structure
inport/export stuff from the main articles? maybe split article into aids (condition) and have 'aids' be about aids in general/overview?
DO THINGS IN CAPITALS BELOW or shift them below 'suggest...'
think up good section names
spellcheck!
anchor old-section titles to newuns
current events tag to current epidemology (moves quite fast)
suggest replace article with this one and then:
drop lang. make sure useful to scientists, but readable by non-scientist. no unnessesary wordage. 'disease progression' rather than 'prognosis', etc.
make sure sciency (CD4+ etc) shit explained inline.
check citations (yuk)
use pyramid wrighting for going from simple --> sciency??????
general tidyage and improvement (picture captions, etc)
MUCH SMALLER LEDE GOETH HERE
introduction[edit]
LESS MINI LEDE ESSENTIALLY GOES HERE
AIDS (condition)[edit]
SUMMARY OF AIDS (THE CONDITION) GOETH HERE
Cause/contraction[edit]

AIDS is the most severe acceleration of infection with HIV. HIV is a retrovirus that primarily infects vital organs of the human immune system such as CD4+ T cells (a subset of T cells), macrophages and dendritic cells. It directly and indirectly destroys CD4+ T cells.[1]
Once HIV has killed so many CD4+ T cells that there are fewer than 200 of these cells per microliter (µL) of blood, cellular immunity is lost. Acute HIV infection progresses over time to clinical latent HIV infection and then to early symptomatic HIV infection and later to AIDS, which is identified either on the basis of the amount of CD4+ T cells remaining in the blood, and/or the presence of certain infections, as noted above.[2]
In the absence of antiretroviral therapy, the median time of progression from HIV infection to AIDS is nine to ten years, and the median survival time after developing AIDS is only 9.2 months.[3] However, the rate of clinical disease progression varies widely between individuals, from two weeks up to 20 years.
Many factors affect the rate of progression. These include factors that influence the body's ability to defend against HIV such as the infected person's general immune function.[4][5] Older people have weaker immune systems, and therefore have a greater risk of rapid disease progression than younger people.
Poor access to health care and the existence of coexisting infections such as tuberculosis also may predispose people to faster disease progression.[3][6][7] The infected person's genetic inheritance plays an important role and some people are resistant to certain strains of HIV. An example of this is people with the homozygous CCR5-Δ32 variation are resistant to infection with certain strains of HIV.[8] HIV is genetically variable and exists as different strains, which cause different rates of clinical disease progression.[9][10][11]
Sexual transmission[edit]
Sexual transmission occurs with the contact between sexual secretions of one person with the rectal, genital or oral mucous membranes of another. Unprotected receptive sexual acts are riskier than unprotected insertive sexual acts, and the risk for transmitting HIV through unprotected anal intercourse is greater than the risk from vaginal intercourse or oral sex.
However, oral sex is not entirely safe, as HIV can be transmitted through both insertive and receptive oral sex.[12][13] Sexual assault greatly increases the risk of HIV transmission as protection is rarely employed and physical trauma to the vagina frequently occurs, facilitating the transmission of HIV.[14]
Other sexually transmitted infections (STI) increase the risk of HIV transmission and infection, because they cause the disruption of the normal epithelial barrier by genital ulceration and/or microulceration; and by accumulation of pools of HIV-susceptible or HIV-infected cells (lymphocytes and macrophages) in semen and vaginal secretions. Epidemiological studies from sub-Saharan Africa, Europe and North America suggest that genital ulcers, such as those caused by syphilis and/or chancroid, increase the risk of becoming infected with HIV by about fourfold. There is also a significant although lesser increase in risk from STIs such as gonorrhea, Chlamydial infection and trichomoniasis, which all cause local accumulations of lymphocytes and macrophages.[15]
Transmission of HIV depends on the infectiousness of the index case and the susceptibility of the uninfected partner. Infectivity seems to vary during the course of illness and is not constant between individuals. An undetectable plasma viral load does not necessarily indicate a low viral load in the seminal liquid or genital secretions.
However, each 10-fold increase in the level of HIV in the blood is associated with an 81% increased rate of HIV transmission.[15][16] Women are more susceptible to HIV-1 infection due to hormonal changes, vaginal microbial ecology and physiology, and a higher prevalence of sexually transmitted diseases.[17][18]
People who have been infected with one strain of HIV can still be infected later on in their lives by other, more virulent strains.
Infection is unlikely in a single encounter. High rates of infection have been linked to a pattern of overlapping long-term romantic relationships. This allows the virus to quickly spread to multiple partners who in turn infect their partners. A pattern of serial monogamy or occasional casual encounters is associated with lower rates of infection.[19]
HIV spreads readily through heterosexual sex in Africa, but less so elsewhere. One possibility being researched is that schistosomiasis, which affects up to 50 per cent of women in parts of Africa, damages the lining of the vagina.[20][21]
Exposure to blood-borne pathogens[edit]

This transmission route is particularly relevant to intravenous drug users, hemophiliacs and recipients of blood transfusions and blood products. Sharing and reusing syringes contaminated with HIV-infected blood represents a major risk for infection with HIV.
Needle sharing is the cause of one third of all new HIV-infections in North America, China, and Eastern Europe. The risk of being infected with HIV from a single prick with a needle that has been used on an HIV-infected person is thought to be about 1 in 150 (see table above). Post-exposure prophylaxis with anti-HIV drugs can further reduce this risk.[22]
This route can also affect people who give and receive tattoos and piercings. Universal precautions are frequently not followed in both sub-Saharan Africa and much of Asia because of both a shortage of supplies and inadequate training.
The WHO estimates that approximately 2.5% of all HIV infections in sub-Saharan Africa are transmitted through unsafe healthcare injections.[23] Because of this, the United Nations General Assembly has urged the nations of the world to implement precautions to prevent HIV transmission by health workers.[24]
The risk of transmitting HIV to blood transfusion recipients is extremely low in developed countries where improved donor selection and HIV screening is performed. However, according to the WHO, the overwhelming majority of the world's population does not have access to safe blood and between 5% and 10% of the world's HIV infections come from transfusion of infected blood and blood products.[25]
Perinatal transmission[edit]
The transmission of the virus from the mother to the child can occur in utero during the last weeks of pregnancy and at childbirth. In the absence of treatment, the transmission rate between a mother and her child during pregnancy, labor and delivery is 25%.
However, when the mother takes antiretroviral therapy and gives birth by caesarean section, the rate of transmission is just 1%.[26] The risk of infection is influenced by the viral load of the mother at birth, with the higher the viral load, the higher the risk. Breastfeeding also increases the risk of transmission by about 4 %.[27]
Cellular explanation[edit]
Pathophysiology[edit]
| This section may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. No cleanup reason has been specified. Please help improve this section if you can; the talk page may contain suggestions. |
The pathophysiology of AIDS is complex, as is the case with all syndromes.[28] Ultimately, HIV causes AIDS by depleting CD4+ T helper lymphocytes. This weakens the immune system and allows opportunistic infections. T lymphocytes are essential to the immune response and without them, the body cannot fight infections or kill cancerous cells. The mechanism of CD4+ T cell depletion differs in the acute and chronic phases.[29]
During the acute phase, HIV-induced cell lysis and killing of infected cells by cytotoxic T cells accounts for CD4+ T cell depletion, although apoptosis may also be a factor. During the chronic phase, the consequences of generalized immune activation coupled with the gradual loss of the ability of the immune system to generate new T cells appear to account for the slow decline in CD4+ T cell numbers.
Although the symptoms of immune deficiency characteristic of AIDS do not appear for years after a person is infected, the bulk of CD4+ T cell loss occurs during the first weeks of infection, especially in the intestinal mucosa, which harbors the majority of the lymphocytes found in the body. [30] The reason for the preferential loss of mucosal CD4+ T cells is that a majority of mucosal CD4+ T cells express the CCR5 coreceptor, whereas a small fraction of CD4+ T cells in the bloodstream do so.[31]
HIV seeks out and destroys CCR5 expressing CD4+ cells during acute infection. A vigorous immune response eventually controls the infection and initiates the clinically latent phase. However, CD4+ T cells in mucosal tissues remain depleted throughout the infection, although enough remain to initially ward off life-threatening infections.
Continuous HIV replication results in a state of generalized immune activation persisting throughout the chronic phase. [32] Immune activation, which is reflected by the increased activation state of immune cells and release of proinflammatory cytokines, results from the activity of several HIV gene products and the immune response to ongoing HIV replication. Another cause is the breakdown of the immune surveillance system of the mucosal barrier caused by the depletion of mucosal CD4+ T cells during the acute phase of disease.[33]
This results in the systemic exposure of the immune system to microbial components of the gut’s normal flora, which in a healthy person is kept in check by the mucosal immune system. The activation and proliferation of T cells that results from immune activation provides fresh targets for HIV infection. However, direct killing by HIV alone cannot account for the observed depletion of CD4+ T cells since only 0.01-0.10% of CD4+ T cells in the blood are infected.
A major cause of CD4+ T cell loss appears to result from their heightened susceptibility to apoptosis when the immune system remains activated. Although new T cells are continuously produced by the thymus to replace the ones lost, the regenerative capacity of the thymus is slowly destroyed by direct infection of its thymocytes by HIV. Eventually, the minimal number of CD4+ T cells necessary to maintain a sufficient immune response is lost, leading to AIDS
Cells affected[edit]
The virus, entering through which ever route, acts primarily on the following cells:[34]
- Lymphoreticular system:
- CD4+ T-Helper cells
- CD4+ Macrophages
- CD4+ Monocytes
- B-lymphocytes
- Certain endothelial cells
- Central nervous system:
- Microglia of the nervous system
- Astrocytes
- Oligodendrocytes
- Neurones - indirectly by the action of cytokines and the gp-120
The effect[edit]
The virus has cytopathic effects but how it does it is still not quite clear. It can remain inactive in these cells for long periods, though. This effect is hypothesized to be due to the CD4-gp120 interaction.[35]
- The most prominent effect of the HIV virus is its T-helper cell suppression and lysis. The cell is simply killed off or deranged to the point of being function-less (they do not respond to foreign antigens). The infected B-cells can not produce enough antibodies either. Thus the immune system collapses leading to the familiar AIDS complications, like infections and neoplasms (vide supra).
- Infection of the cells of the CNS cause acute aseptic meningitis, subacute encephalitis, vacuolar myelopathy and peripheral neuropathy. Later it leads to even AIDS dementia complex.
- The CD4-gp120 interaction (vide supra) is also permissive to other viruses like Cytomegalovirus, Hepatitis virus, Herpes simplex virus, etc. These viruses lead to further cell damage i.e. cytopathy.
Molecular basis[edit]
SUMMARY GOETH HERE
For details, see:
Effects[edit]
THIS BIT CAME FROM SYMPTOMS

The symptoms of AIDS are primarily the result of conditions that do not normally develop in individuals with healthy immune systems. Most of these conditions are infections caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites that are normally controlled by the elements of the immune system that HIV damages.
Opportunistic infections are common in people with AIDS.[36] HIV affects nearly every organ system.
People with AIDS also have an increased risk of developing various cancers such as Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical cancer and cancers of the immune system known as lymphomas. Additionally, people with AIDS often have systemic symptoms of infection like fevers, sweats (particularly at night), swollen glands, chills, weakness, and weight loss.[37][38] The specific opportunistic infections that AIDS patients develop depend in part on the prevalence of these infections in the geographic area in which the patient lives.

Pulmonary infections[edit]

Pneumocystis pneumonia (originally known as Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, and still abbreviated as PCP, which now stands for Pneumocystis pneumonia) is relatively rare in healthy, immunocompetent people, but common among HIV-infected individuals. It is caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii.
Before the advent of effective diagnosis, treatment and routine prophylaxis in Western countries, it was a common immediate cause of death. In developing countries, it is still one of the first indications of AIDS in untested individuals, although it does not generally occur unless the CD4 count is less than 200 cells per µL of blood.[39]
Tuberculosis (TB) is unique among infections associated with HIV because it is transmissible to immunocompetent people via the respiratory route, is easily treatable once identified, may occur in early-stage HIV disease, and is preventable with drug therapy. However, multidrug resistance is a potentially serious problem.
Even though its incidence has declined because of the use of directly observed therapy and other improved practices in Western countries, this is not the case in developing countries where HIV is most prevalent. In early-stage HIV infection (CD4 count >300 cells per µL), TB typically presents as a pulmonary disease. In advanced HIV infection, TB often presents atypically with extrapulmonary (systemic) disease a common feature. Symptoms are usually constitutional and are not localized to one particular site, often affecting bone marrow, bone, urinary and gastrointestinal tracts, liver, regional lymph nodes, and the central nervous system.[40]
Gastrointestinal infections[edit]
Esophagitis is an inflammation of the lining of the lower end of the esophagus (gullet or swallowing tube leading to the stomach). In HIV infected individuals, this is normally due to fungal (candidiasis) or viral (herpes simplex-1 or cytomegalovirus) infections. In rare cases, it could be due to mycobacteria.[41]
Unexplained chronic diarrhea in HIV infection is due to many possible causes, including common bacterial (Salmonella, Shigella, Listeria or Campylobacter) and parasitic infections; and uncommon opportunistic infections such as cryptosporidiosis, microsporidiosis, Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) and viruses,[42] astrovirus, adenovirus, rotavirus and cytomegalovirus, (the latter as a course of colitis).
In some cases, diarrhea may be a side effect of several drugs used to treat HIV, or it may simply accompany HIV infection, particularly during primary HIV infection. It may also be a side effect of antibiotics used to treat bacterial causes of diarrhea (common for Clostridium difficile). In the later stages of HIV infection, diarrhea is thought to be a reflection of changes in the way the intestinal tract absorbs nutrients, and may be an important component of HIV-related wasting.[43]
Neurological and psychiatric involvement[edit]
HIV infection may lead to a variety of neuropsychiatric sequelae, either by infection of the now susceptible nervous system by organisms, or as a direct consequence of the illness itself.
Toxoplasmosis is a disease caused by the single-celled parasite called Toxoplasma gondii; it usually infects the brain, causing toxoplasma encephalitis, but it can also infect and cause disease in the eyes and lungs.[44] Cryptococcal meningitis is an infection of the meninx (the membrane covering the brain and spinal cord) by the fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. It can cause fevers, headache, fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. Patients may also develop seizures and confusion; left untreated, it can be lethal.
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a demyelinating disease, in which the gradual destruction of the myelin sheath covering the axons of nerve cells impairs the transmission of nerve impulses. It is caused by a virus called JC virus which occurs in 70% of the population in latent form, causing disease only when the immune system has been severely weakened, as is the case for AIDS patients. It progresses rapidly, usually causing death within months of diagnosis.[45]
AIDS dementia complex (ADC) is a metabolic encephalopathy induced by HIV infection and fueled by immune activation of HIV infected brain macrophages and microglia. These cells are productively infected by HIV and secrete neurotoxins of both host and viral origin.[46] Specific neurological impairments are manifested by cognitive, behavioral, and motor abnormalities that occur after years of HIV infection and are associated with low CD4+ T cell levels and high plasma viral loads.
Prevalence is 10–20% in Western countries[47] but only 1–2% of HIV infections in India.[48][49] This difference is possibly due to the HIV subtype in India. AIDS related mania is sometimes seen in patients with advanced HIV illness; it presents with more irritability and cognitive impairment and less euphoria than a manic episode associated with true bipolar disorder. Unlike the latter condition, it may have a more chronic course. This syndrome is less often seen with the advent of multi-drug therapy.
Tumors and malignancies[edit]
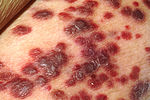
Patients with HIV infection have substantially increased incidence of several cancers. This is primarily due to co-infection with an oncogenic DNA virus, especially Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), and human papillomavirus (HPV).[50][51]
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is the most common tumor in HIV-infected patients. The appearance of this tumor in young homosexual men in 1981 was one of the first signals of the AIDS epidemic. Caused by a gammaherpes virus called Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus (KSHV), it often appears as purplish nodules on the skin, but can affect other organs, especially the mouth, gastrointestinal tract, and lungs.
High-grade B cell lymphomas such as Burkitt's lymphoma, Burkitt's-like lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and primary central nervous system lymphoma present more often in HIV-infected patients. These particular cancers often foreshadow a poor prognosis. In some cases these lymphomas are AIDS-defining. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) or KSHV cause many of these lymphomas.
Cervical cancer in HIV-infected women is considered AIDS-defining. It is caused by human papillomavirus (HPV).[52]
In addition to the AIDS-defining tumors listed above, HIV-infected patients are at increased risk of certain other tumors, such as Hodgkin's disease and anal and rectal carcinomas. However, the incidence of many common tumors, such as breast cancer or colon cancer, does not increase in HIV-infected patients. In areas where HAART is extensively used to treat AIDS, the incidence of many AIDS-related malignancies has decreased, but at the same time malignant cancers overall have become the most common cause of death of HIV-infected patients.[53]
Other opportunistic infections[edit]
AIDS patients often develop opportunistic infections that present with non-specific symptoms, especially low-grade fevers and weight loss. These include infection with Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare and cytomegalovirus (CMV). CMV can cause colitis, as described above, and CMV retinitis can cause blindness.
Penicilliosis due to Penicillium marneffei is now the third most common opportunistic infection (after extrapulmonary tuberculosis and cryptococcosis) in HIV-positive individuals within the endemic area of Southeast Asia.[54]
Prognosis[edit]
Without treatment, the net median survival time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the HIV subtype,[55] and the median survival rate after diagnosis of AIDS in resource-limited settings where treatment is not available ranges between 6 and 19 months, depending on the study.[56] In areas where it is widely available, the development of HAART as effective therapy for HIV infection and AIDS reduced the death rate from this disease by 80%, and raised the life expectancy for a newly diagnosed HIV-infected person to about 20 years.[57]
As new treatments continue to be developed and because HIV continues to evolve resistance to treatments, estimates of survival time are likely to continue to change. Without antiretroviral therapy, death normally occurs within a year.[3] Most patients die from opportunistic infections or malignancies associated with the progressive failure of the immune system.[58] The rate of clinical disease progression varies widely between individuals and has been shown to be affected by many factors such as host susceptibility and immune function[4][5][8] health care and co-infections,[3][58] as well as which particular strain of the virus is involved.[10][59][60]
AIDS (pandemic)[edit]
SUMMARY OF AIDS THE PANDEMIC GOES HERE
history[edit]
AIDS was first reported June 5, 1981, when the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recorded a cluster of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (now still classified as PCP but known to be caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii) in five homosexual men in Los Angeles.[61] In the beginning, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) did not have an official name for the disease, often referring to it by way of the diseases that were associated with it, for example, lymphadenopathy, the disease after which the discoverers of HIV originally named the virus.[62][63] They also used Kaposi's Sarcoma and Opportunistic Infections, the name by which a task force had been set up in 1981.[64] In the general press, the term GRID, which stood for Gay-related immune deficiency, had been coined.[65] The CDC, in search of a name, and looking at the infected communities coined “the 4H disease,” as it seemed to single out Haitians, homosexuals, hemophiliacs, and heroin users.[66] However, after determining that AIDS was not isolated to the homosexual community,[64] the term GRID became misleading and AIDS was introduced at a meeting in July 1982.[67] By September 1982 the CDC started using the name AIDS, and properly defined the illness.[68]
A more controversial theory known as the OPV AIDS hypothesis suggests that the AIDS epidemic was inadvertently started in the late 1950s in the Belgian Congo by Hilary Koprowski's research into a poliomyelitis vaccine.[69][70] According to scientific consensus, this scenario is not supported by the available evidence.[71][72][73]
A recent study states that HIV probably moved from Africa to Haiti and then entered the United States around 1969.[74]
current epidemology[edit]
| This user page needs to be updated. Please help update this user page to reflect recent events or newly available information. |
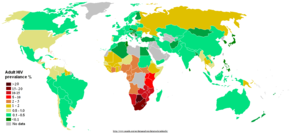
The AIDS pandemic can also be seen as several epidemics of separate subtypes; the major factors in its spread are sexual transmission and vertical transmission from mother to child at birth and through breast milk.[75] Despite recent, improved access to antiretroviral treatment and care in many regions of the world, the AIDS pandemic claimed an estimated 2.1 million (range 1.9–2.4 million) lives in 2007 of which an estimated 330,000 were children under 15 years.[55] Globally, an estimated 33.2 million people lived with HIV in 2007, including 2.5 million children. An estimated 2.5 million (range 1.8–4.1 million) people were newly infected in 2007, including 420,000 children.[55]
Sub-Saharan Africa remains by far the worst affected region. In 2007 it contained an estimated 68% of all people living with AIDS and 76% of all AIDS deaths, with 1.7 million new infections bringing the number of people living with HIV to 22.5 million, and with 11.4 million AIDS orphans living in the region. Unlike other regions, most people living with HIV in sub-Saharan Africa in 2007 (61%) were women. Adult prevalence in 2007 was an estimated 5.0%, and AIDS continued to be the single largest cause of mortality in this region.[55] South Africa has the largest population of HIV patients in the world, followed by Nigeria and India.[76] South & South East Asia are second worst affected; in 2007 this region contained an estimated 18% of all people living with AIDS, and an estimated 300,000 deaths from AIDS.[55] India has an estimated 2.5 million infections and an estimated adult prevalence of 0.36%.[55] Life expectancy has fallen dramatically in the worst-affected countries; for example, in 2006 it was estimated that it had dropped from 65 to 35 years in Botswana.[75]
impact[edit]
DEATH COUNT GOES HERE
Economic impact[edit]

HIV and AIDS affects economic growth by reducing the availability of human capital.[77] Without proper nutrition, health care and medicine that is available in developed countries, large numbers of people are falling victim to AIDS. They will not only be unable to work, but will also require significant medical care. The forecast is that this will likely cause a collapse of economies and societies in countries with a significant AIDS population. In some heavily infected areas, the epidemic has left behind many orphans cared for by elderly grandparents.[78]
The increased mortality in this region will result in a smaller skilled population and labor force. This smaller labor force will be predominantly young people, with reduced knowledge and work experience leading to reduced productivity. An increase in workers’ time off to look after sick family members or for sick leave will also lower productivity. Increased mortality will also weaken the mechanisms that generate human capital and investment in people, through loss of income and the death of parents. By killing off mainly young adults, AIDS seriously weakens the taxable population, reducing the resources available for public expenditures such as education and health services not related to AIDS resulting in increasing pressure for the state's finances and slower growth of the economy. This results in a slower growth of the tax base, an effect that will be reinforced if there are growing expenditures on treating the sick, training (to replace sick workers), sick pay and caring for AIDS orphans. This is especially true if the sharp increase in adult mortality shifts the responsibility and blame from the family to the government in caring for these orphans.[78]
On the level of the household, AIDS results in both the loss of income and increased spending on healthcare by the household. The income effects of this lead to spending reduction as well as a substitution effect away from education and towards healthcare and funeral spending. A study in Côte d'Ivoire showed that households with an HIV/AIDS patient spent twice as much on medical expenses as other households.[79]
future trends[edit]
human responce[edit]
WHY SO LARGE A RESPONCE?
RE-RE-FACTOR: SHOULD FLOW: TREATMENT FOR AIDS INFECTED, SUPPRESSION OF EPIDEMIC (LIMITATION OF SPREAD, PREVENTION OF NEW STRAINS), AMELIORATION OF DAMAGE(?), RESEARCH FOR CURE
in individual[edit]
diagnosis[edit]
DIAGNOSIS
treatment[edit]
TREATMENT
alternative (not used) treatments[edit]
research[edit]
as epidemic[edit]
prevention[edit]
PREVENTION
OR MAYBE 'PREVENTION' AND CONTRACEPTION SHOULD GO UNDERR INDIVIDUAL, WHILST EPIDEMOLOGICAL PREVENTION BRIEFELY MENTIONS THOSE TWO, PLUS WORK IN AFRICA ETC?
contraceptive[edit]
no eaty tastey monkey[edit]
global co-ordination[edit]
UN, COUNTRY-BY-COUNTRY, ETC?
aids in...[edit]
AIDS in science[edit]
aids and homosexuals[edit]
Active pursuit of HIV infection[edit]
A subculture of homosexual men desire and actively pursue HIV infection by seeking partners who are HIV-positive and voluntarily having unprotected intercourse with them. In slang terms, those who seek infection are called bugchasers and those who infect them are called giftgivers.[80] This phenomenon should be distinguished from barebacking, which is the preference for unprotected intercourse without the active desire for HIV infection.
The exact extent of practice remains largely unknown. Not all those who self-identify as part of this subculture are actually intent on spreading HIV.[81] Some bugchasers try to connect with giftgivers via the Internet.[82] Other bugchasers organize and participate in "bug parties" or "conversion parties," sex parties where HIV positive and negative men engage in unprotected sex, in hopes of acquiring HIV ("getting the gift").[83]
aids in society[edit]
Stigma[edit]

AIDS stigma exists around the world in a variety of ways, including ostracism, rejection, discrimination and avoidance of HIV infected people; compulsory HIV testing without prior consent or protection of confidentiality; violence against HIV infected individuals or people who are perceived to be infected with HIV; and the quarantine of HIV infected individuals.[84] Stigma-related violence or the fear of violence prevents many people from seeking HIV testing, returning for their results, or securing treatment, possibly turning what could be a manageable chronic illness into a death sentence and perpetuating the spread of HIV.[85]
AIDS stigma has been further divided into the following three categories:
- Instrumental AIDS stigma—a reflection of the fear and apprehension that are likely to be associated with any deadly and transmissible illness.[86]
- Symbolic AIDS stigma—the use of HIV/AIDS to express attitudes toward the social groups or lifestyles perceived to be associated with the disease.[86]
- Courtesy AIDS stigma—stigmatization of people connected to the issue of HIV/AIDS or HIV- positive people.[87]
Often, AIDS stigma is expressed in conjunction with one or more other stigmas, particularly those associated with homosexuality, bisexuality, promiscuity, prostitution, and intravenous drug use.
In many developed countries, there is an association between AIDS and homosexuality or bisexuality, and this association is correlated with higher levels of sexual prejudice such as anti-homosexual attitudes.[88] There is also a perceived association between AIDS and all male-male sexual behavior, including sex between uninfected men.[86]
AIDS denialism[edit]
A small number of activists question the connection between HIV and AIDS,[89] the existence of HIV,[90] or the validity of current treatment methods (even going so far as to claim that the drug therapy itself was the cause of AIDS deaths). Though these claims have been examined and thoroughly rejected by the scientific community,[91] they continue to be promulgated through the Internet[92] and have had a significant political impact. In South Africa, former President Thabo Mbeki's embrace of AIDS denialism resulted in an ineffective governmental response to the AIDS epidemic that has been blamed for hundreds of thousands of AIDS-related deaths.[93][94]
trivia[edit]
KILLED FREDDY MERCURY ETC
see also[edit]
misc/unincluded[edit]
aids has been cured trivia?
other aids names (htlv-iii, arv, gay-diesase, skinny, etc) lede?
other aids (irradiation, etc) lede?
misconceptions (under specific bit (eg, spreading), or one section?)
Misconceptions[edit]
A number of misconceptions have arisen surrounding HIV/AIDS. Three of the most common are that AIDS can spread through casual contact, that sexual intercourse with a virgin will cure AIDS, and that HIV can infect only homosexual men and drug users. Other misconceptions are that any act of anal intercourse between gay men can lead to AIDS infection, and that open discussion of homosexuality and HIV in schools will lead to increased rates of homosexuality and AIDS.[95]
- ^ Alimonti JB, Ball TB, Fowke KR (2003). "Mechanisms of CD4+ T lymphocyte cell death in human immunodeficiency virus infection and AIDS". J. Gen. Virol. 84 (7): 1649–1661. doi:10.1099/vir.0.19110-0. PMID 12810858.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ An Atlas of Differential Diagnosis in HIV Disease, Second Edition. CRC Press-Parthenon Publishers. 2003. pp. 22–27. ISBN 1-84214-026-4.
- ^ a b c d Morgan D, Mahe C, Mayanja B, Okongo JM, Lubega R, Whitworth JA (2002). "HIV-1 infection in rural Africa: is there a difference in median time to AIDS and survival compared with that in industrialized countries?". AIDS. 16 (4): 597–632. doi:10.1097/00002030-200203080-00011. PMID 11873003. S2CID 35450422.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Clerici M, Balotta C, Meroni L; et al. (1996). "Type 1 cytokine production and low prevalence of viral isolation correlate with long-term non progression in HIV infection". AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses. 12 (11): 1053–1061. doi:10.1089/aid.1996.12.1053. PMID 8827221.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Morgan D, Mahe C, Mayanja B, Whitworth JA (2002). "Progression to symptomatic disease in people infected with HIV-1 in rural Uganda: prospective cohort study". BMJ. 324 (7331): 193–196. doi:10.1136/bmj.324.7331.193. PMC 64788. PMID 11809639.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Gendelman HE, Phelps W, Feigenbaum L; et al. (1986). "Transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat sequences by DNA viruses". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 83 (24): 9759–9763. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.24.9759. PMC 387220. PMID 2432602.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bentwich Z, Kalinkovich, A, Weisman Z (1995). "Immune activation is a dominant factor in the pathogenesis of African AIDS". Immunol. Today. 16 (4): 187–191. doi:10.1016/0167-5699(95)80119-7. PMID 7734046.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Tang J, Kaslow RA (2003). "The impact of host genetics on HIV infection and disease progression in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy". AIDS. 17 (Suppl 4): S51–S60. doi:10.1097/00002030-200317004-00006. PMID 15080180.
- ^ Quiñones-Mateu ME, Mas A, Lain de Lera T, Soriano V, Alcami J, Lederman MM, Domingo E (1998). "LTR and tat variability of HIV-1 isolates from patients with divergent rates of disease progression". Virus Research. 57 (1): 11–20. doi:10.1016/s0168-1702(98)00082-3. PMID 9833881.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Campbell GR, Pasquier E, Watkins J; et al. (2004). "The glutamine-rich region of the HIV-1 Tat protein is involved in T-cell apoptosis". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (46): 48197–48204. doi:10.1074/jbc.M406195200. PMID 15331610.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Kaleebu P, French N, Mahe C; et al. (2002). "Effect of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 envelope subtypes A and D on disease progression in a large cohort of HIV-1-positive persons in Uganda". J. Infect. Dis. 185 (9): 1244–1250. doi:10.1086/340130. PMID 12001041.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Rothenberg RB, Scarlett M, del Rio C, Reznik D, O'Daniels C (1998). "Oral transmission of HIV". AIDS. 12 (16): 2095–2105. doi:10.1097/00002030-199816000-00004. PMID 9833850. S2CID 35972115.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Mastro TD, de Vincenzi I (1996). "Probabilities of sexual HIV-1 transmission". AIDS. 10 (Suppl A): S75–S82. doi:10.1097/00002030-199601001-00011. PMID 8883613. S2CID 39456339.
- ^ Koenig MA, Zablotska I, Lutalo T, Nalugoda F, Wagman J, Gray R (2004). "Coerced first intercourse and reproductive health among adolescent women in Rakai, Uganda". Int Fam Plan Perspect. 30 (4): 156–63. doi:10.1363/ifpp.30.156.04. PMID 15590381.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Laga M, Nzila N, Goeman J (1991). "The interrelationship of sexually transmitted diseases and HIV infection: implications for the control of both epidemics in Africa". AIDS. 5 (Suppl 1): S55–S63. PMID 1669925.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Tovanabutra S, Robison V, Wongtrakul J; et al. (2002). "Male viral load and heterosexual transmission of HIV-1 subtype E in northern Thailand". J. Acquir. Immune. Defic. Syndr. 29 (3): 275–283. doi:10.1097/00126334-200203010-00008. PMID 11873077.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Sagar M, Lavreys L, Baeten JM; et al. (2004). "Identification of modifiable factors that affect the genetic diversity of the transmitted HIV-1 population". AIDS. 18 (4): 615–619. doi:10.1097/00002030-200403050-00005. PMID 15090766. S2CID 11038376.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lavreys L, Baeten JM, Martin HL; et al. (March 2004). "Hormonal contraception and risk of HIV-1 acquisition: results of a 10-year prospective study". AIDS. 18 (4): 695–7. doi:10.1097/00002030-200403050-00017. PMID 15090778. S2CID 8624614.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Epstein, Helen (2007). The invisible cure: Africa, the West, and the fight against AIDS. New York: Farrar, Straus, and Giroux. ISBN 978-0-374-28152-6.
- ^ Parasitic worms may boost African HIV rates
- ^ Agnès-Laurence Chenine, Ela Shai-Kobiler, Lisa N. Steele, Helena Ong, Peter Augostini, Ruijiang Song, Sandra J. Lee, Patrick Autissier, Ruth M. Ruprecht, W. Evan Secor Acute Schistosoma mansoni Infection Increases Susceptibility to Systemic SHIV Clade C Infection in Rhesus Macaques after Mucosal Virus Exposure PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000265
- ^ Fan H (2005). Fan, H., Conner, R. F. and Villarreal, L. P. eds (ed.). AIDS: science and society (4th ed.). Boston, MA: Jones and Bartlett Publishers. ISBN 0-7637-0086-X.
{{cite book}}:|editor=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ "WHO, UNAIDS Reaffirm HIV as a Sexually Transmitted Disease". WHO. 2003-03-17. Retrieved 2006-01-17.
- ^ "Financial Resources Required to Achieve, Universal Access to HIV Prevention, Treatment Care and Support" (PDF). UNAIDS. Retrieved 2008-04-11.
- ^ "Blood safety....for too few". WHO. 2001. Retrieved 2006-01-17.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Coovadiawas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Coovadia HM, Bland RM (2007). "Preserving breastfeeding practice through the HIV pandemic". Trop. Med. Int. Health. 12 (9): 1116–1133. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3156.2007.01895.x. PMID 17714431. S2CID 308933.
- ^ Guss DA (1994). "The acquired immune deficiency syndrome: an overview for the emergency physician, Part 1". J Emerg Med. 12 (3): 375–84. doi:10.1016/0736-4679(94)90281-x. PMID 8040596.
- ^ Hel Z, McGhee JR, Mestecky J (June 2006). "HIV infection: first battle decides the war". Trends Immunol. 27 (6): 274–81. doi:10.1016/j.it.2006.04.007. PMID 16679064.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Mehandru S, Poles MA, Tenner-Racz K, Horowitz A, Hurley A, Hogan C, Boden D, Racz P, Markowitz M (September 2004). "Primary HIV-1 infection is associated with preferential depletion of CD4+ T lymphocytes from effector sites in the gastrointestinal tract". J. Exp. Med. 200 (6): 761–70. doi:10.1084/jem.20041196. PMC 2211967. PMID 15365095.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Brenchley JM, Schacker TW, Ruff LE, Price DA, Taylor JH, Beilman GJ, Nguyen PL, Khoruts A, Larson M, Haase AT, Douek DC (September 2004). "CD4+ T cell depletion during all stages of HIV disease occurs predominantly in the gastrointestinal tract". J. Exp. Med. 200 (6): 749–59. doi:10.1084/jem.20040874. PMC 2211962. PMID 15365096.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Appay V, Sauce D (January 2008). "Immune activation and inflammation in HIV-1 infection: causes and consequences". J. Pathol. 214 (2): 231–41. doi:10.1002/path.2276. PMID 18161758. S2CID 26830006.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Brenchley JM, Price DA, Schacker TW, Asher TE, Silvestri G, Rao S, Kazzaz Z, Bornstein E, Lambotte O, Altmann D, Blazar BR, Rodriguez B, Teixeira-Johnson L, Landay A, Martin JN, Hecht FM, Picker LJ, Lederman MM, Deeks SG, Douek DC (December 2006). "Microbial translocation is a cause of systemic immune activation in chronic HIV infection". Nat. Med. 12 (12): 1365–71. doi:10.1038/nm1511. PMID 17115046. S2CID 32845860.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Textbook of Pathology by Harsh Mohan, ISBN 81-8061-368-2
- ^ Textbook of Pathology by Harsh Mohan, ISBN 81-8061-368-2
- ^ Holmes CB, Losina E, Walensky RP, Yazdanpanah Y, Freedberg KA (2003). "Review of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-related opportunistic infections in sub-Saharan Africa". Clin. Infect. Dis. 36 (5): 656–662. doi:10.1086/367655. PMID 12594648. S2CID 18536260.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Guss DA (1994). "The acquired immune deficiency syndrome: an overview for the emergency physician, Part 1". J. Emerg. Med. 12 (3): 375–384. doi:10.1016/0736-4679(94)90281-x. PMID 8040596.
- ^ Guss DA (1994). "The acquired immune deficiency syndrome: an overview for the emergency physician, Part 2". J. Emerg. Med. 12 (4): 491–497. doi:10.1016/0736-4679(94)90346-8. PMID 7963396.
- ^ Feldman C (2005). "Pneumonia associated with HIV infection". Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 18 (2): 165–170. doi:10.1097/01.qco.0000160907.79437.5a. PMID 15735422. S2CID 31827307.
- ^ Decker CF, Lazarus A (2000). "Tuberculosis and HIV infection. How to safely treat both disorders concurrently". Postgrad Med. 108 (2): 57–60, 65–68. doi:10.3810/pgm.2000.08.1181. PMID 10951746. S2CID 213057.
- ^ Zaidi SA, Cervia JS (2002). "Diagnosis and management of infectious esophagitis associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection". J. Int. Assoc. Physicians AIDS Care (Chic Ill). 1 (2): 53–62. doi:10.1177/154510970200100204. PMID 12942677. S2CID 38823534.
- ^ Pollok RC (2001). "Viruses causing diarrhoea in AIDS". Novartis Found. Symp. Novartis Foundation Symposia. 238: 276–83, discussion 283–8. doi:10.1002/0470846534.ch17. ISBN 9780471496632. PMID 11444032.
- ^ Guerrant RL, Hughes JM, Lima NL, Crane J (1990). "Diarrhea in developed and developing countries: magnitude, special settings, and etiologies". Rev. Infect. Dis. 12 (Suppl 1): S41–S50. doi:10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_1.s41. PMC 7792920. PMID 2406855.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Luft BJ, Chua A (2000). "Central Nervous System Toxoplasmosis in HIV Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy". Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2 (4): 358–362. doi:10.1007/s11908-000-0016-x. PMID 11095878. S2CID 30642847.
- ^ Sadler M, Nelson MR (1997). "Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in HIV". Int. J. STD AIDS. 8 (6): 351–357. doi:10.1258/0956462971920181. PMID 9179644.
- ^ Gray F, Adle-Biassette H, Chrétien F, Lorin de la Grandmaison G, Force G, Keohane C (2001). "Neuropathology and neurodegeneration in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Pathogenesis of HIV-induced lesions of the brain, correlations with HIV-associated disorders and modifications according to treatments". Clin. Neuropathol. 20 (4): 146–155. PMID 11495003.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Grant I, Sacktor H, McArthur J (2005). "HIV neurocognitive disorders" (PDF). In H. E. Gendelman, I. Grant, I. Everall, S. A. Lipton, and S. Swindells. (ed.) (ed.). The Neurology of AIDS (2nd ed.). London, UK: Oxford University Press. pp. 357–373. ISBN 0-19-852610-5.
{{cite book}}:|editor=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Satishchandra P, Nalini A, Gourie-Devi M; et al. (2000). "Profile of neurologic disorders associated with HIV/AIDS from Bangalore, South India (1989–1996)". Indian J. Med. Res. 11: 14–23. PMID 10793489.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Wadia RS, Pujari SN, Kothari S, Udhar M, Kulkarni S, Bhagat S, Nanivadekar A (2001). "Neurological manifestations of HIV disease". J. Assoc. Physicians India. 49: 343–348. PMID 11291974.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Boshoff C, Weiss R (2002). "AIDS-related malignancies". Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2 (5): 373–382. doi:10.1038/nrc797. PMID 12044013. S2CID 13513517.
- ^ Yarchoan R, Tosatom G, Littlem RF (2005). "Therapy insight: AIDS-related malignancies — the influence of antiviral therapy on pathogenesis and management". Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2 (8): 406–415. doi:10.1038/ncponc0253. PMID 16130937. S2CID 23476060.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Palefsky J (2007). "Human papillomavirus infection in HIV-infected persons". Top HIV Med. 15 (4): 130–3. PMID 17720998.
- ^ Bonnet F, Lewden C, May T; et al. (2004). "Malignancy-related causes of death in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy". Cancer. 101 (2): 317–324. doi:10.1002/cncr.20354. PMID 15241829. S2CID 79554735.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Skoulidis F, Morgan MS, MacLeod KM (2004). "Penicillium marneffei: a pathogen on our doorstep?". J. R. Soc. Med. 97 (2): 394–396. doi:10.1177/014107680409700811. PMC 1079563. PMID 15286196.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f UNAIDS, WHO (December 2007). "2007 AIDS epidemic update" (PDF). Retrieved 2008-03-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Zwahlen M, Egger M (2006). "Progression and mortality of untreated HIV-positive individuals living in resource-limited settings: update of literature review and evidence synthesis" (Document).
{{cite document}}: Cite document requires|publisher=(help); Unknown parameter|accessdate=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|url=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|version=ignored (help) - ^ Knoll B, Lassmann B, Temesgen Z (2007). "Current status of HIV infection: a review for non-HIV-treating physicians". Int J Dermatol. 46 (12): 1219–28. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2007.03520.x. PMID 18173512. S2CID 26248996.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Lawn SD (2004). "AIDS in Africa: the impact of coinfections on the pathogenesis of HIV-1 infection". J. Infect. Dis. 48 (1): 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2003.09.001. PMID 14667787.
- ^ Campbell GR, Watkins JD, Esquieu D, Pasquier E, Loret EP, Spector SA (2005). "The C terminus of HIV-1 Tat modulates the extent of CD178-mediated apoptosis of T cells". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (46): 38376–39382. doi:10.1074/jbc.M506630200. PMID 16155003.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Senkaali D, Muwonge R, Morgan D, Yirrell D, Whitworth J, Kaleebu P (2005). "The relationship between HIV type 1 disease progression and V3 serotype in a rural Ugandan cohort". AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses. 20 (9): 932–937. doi:10.1089/aid.2004.20.932. PMID 15585080.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Gottlieb MS (2006). "Pneumocystis pneumonia--Los Angeles. 1981". Am J Public Health. 96 (6): 980–1, discussion 982–3. doi:10.2105/ajph.96.6.980. PMC 1470612. PMID 16714472.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
MMWR1982awas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Barrewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Centers for Disease Control (CDC) (1982). "Opportunistic infections and Kaposi's sarcoma among Haitians in the United States". MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 31 (26): 353–354, 360–361. PMID 6811853.
- ^ Altman LK (1982-05-11). "New homosexual disorder worries officials". The New York Times.
- ^ "Making Headway Under Hellacious Circumstances" (PDF). American Association for the Advancement of Science. 2006-07-28. Retrieved 2008-06-23.
- ^ Kher U (1982-07-27). "A Name for the Plague". Time. Retrieved 2008-03-10.
- ^ Centers for Disease Control (CDC) (1982). "Update on acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)—United States". MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 31 (37): 507–508, 513–514. PMID 6815471.
- ^ Curtis T (1992). "The origin of AIDS". Rolling Stone. No. 626. pp. 54–59, 61, 106, 108. Retrieved 2008-03-10.
- ^ Hooper E (1999). The River : A Journey to the Source of HIV and AIDS (1st ed.). Boston, MA: Little Brown & Co. pp. 1–1070. ISBN 0-316-37261-7.
- ^ Worobey M, Santiago ML, Keele BF; et al. (2004). "Origin of AIDS: contaminated polio vaccine theory refuted". Nature. 428 (6985): 820. doi:10.1038/428820a. PMID 15103367. S2CID 4418410.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Berry N, Jenkins A, Martin J; et al. (2005). "Mitochondrial DNA and retroviral RNA analyses of archival oral polio vaccine (OPV CHAT) materials: evidence of macaque nuclear sequences confirms substrate identity". Vaccine. 23 (14): 1639–1648. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.10.038. PMID 15705467.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Oral Polio Vaccine and HIV / AIDS: Questions and Answers". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2004-03-23. Retrieved 2006-11-20.
- ^ Gilbert MT, Rambaut A, Wlasiuk G, Spira TJ, Pitchenik AE, Worobey M (2007). "The emergence of HIV/AIDS in the Americas and beyond". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104 (47): 18566–70. doi:10.1073/pnas.0705329104. PMC 2141817. PMID 17978186.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Kallings LO (2008). "The first postmodern pandemic: 25 years of HIV/AIDS". J Intern Med. 263 (3): 218–43. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2007.01910.x. PMID 18205765.
- ^ McNeil DG Jr (2007-11-20). "U.N. agency to say it overstated extent of H.I.V. cases by millions". New York Times. Retrieved 2008-03-18.
- ^ Bell C, Devarajan S, Gersbach H (2003). "The long-run economic costs of AIDS: theory and an application to South Africa" (Document).
{{cite document}}: Cite document requires|publisher=(help); Unknown parameter|accessdate=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|url=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|version=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Greener R (2002). "AIDS and macroeconomic impact". In S, Forsyth (ed.) (ed.). State of The Art: AIDS and Economics. IAEN. pp. 49–55.
{{cite book}}:|editor=has generic name (help) - ^
Over M (1992). "The macroeconomic impact of AIDS in Sub-Saharan Africa, Population and Human Resources Department" (Document). The World Bank.
{{cite document}}: Unknown parameter|accessdate=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|url=ignored (help) - ^ Moskowitz DA, Roloff ME (2007). "The existence of a bug chasing subculture". Cult Health Sex. 9 (4): 347–57. doi:10.1080/13691050600976296. PMID 17612955. S2CID 31893571.
- ^ Grov C, Parsons JT (December 2006). "Bug chasing and gift giving: the potential for HIV transmission among barebackers on the internet". AIDS Educ Prev. 18 (6): 490–503. doi:10.1521/aeap.2006.18.6.490. PMID 17166076.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Graydon M (2007). "Don't bother to wrap it: online Giftgiver and Bugchaser newsgroups, the social impact of gift exchanges and the 'carnivalesque'". Cult Health Sex. 9 (3): 277–92. doi:10.1080/13691050601124649. PMID 17457731. S2CID 20164022.
- ^ Dean, T., 2008. "Breeding Culture: barebacking, Bugchasing, Giftgiving". The Massachusetts Review, Vol. 49(1), pp. 80-94.
- ^ "The impact of AIDS on people and societies" (PDF). 2006 Report on the global AIDS epidemic. UNAIDS. 2006. Retrieved 2006-06-14.
- ^ Ogden J, Nyblade L (2005). "Common at its core: HIV-related stigma across contexts" (PDF). International Center for Research on Women. Retrieved 2007-02-15.
- ^ a b c Herek GM, Capitanio JP (1999). "AIDS Stigma and sexual prejudice" (PDF). American Behavioral Scientist. 42 (7): 1130–1147. doi:10.1177/0002764299042007006. S2CID 143508360. Retrieved 2006-03-27.
- ^ Snyder M, Omoto AM, Crain AL (1999). "Punished for their good deeds: stigmatization for AIDS volunteers". American Behavioral Scientist. 42 (7): 1175–1192. doi:10.1177/0002764299042007009. S2CID 144929159.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Herek GM, Capitanio JP, Widaman KF (2002). "HIV-related stigma and knowledge in the United States: prevalence and trends, 1991-1999" (PDF). Am J Public Health. 92 (3): 371–7. doi:10.2105/ajph.92.3.371. PMC 1447082. PMID 11867313. Retrieved 2008-03-10.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Duesberg PH (1988). "HIV is not the cause of AIDS". Science. 241 (4865): 514, 517. doi:10.1126/science.3399880. PMID 3399880.
- ^ Papadopulos-Eleopulos E, Turner VF, Papadimitriou J; et al. (2004). "A critique of the Montagnier evidence for the HIV/AIDS hypothesis". Med Hypotheses. 63 (4): 597–601. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2004.03.025. PMID 15325002.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ For evidence of the scientific consensus that HIV is the cause of AIDS, see (for example):
- "The Evidence That HIV Causes AIDS". National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. 2003. Retrieved 2008-12-20.
- "The Durban Declaration". Nature. 406 (6791): 15–6. 2000. doi:10.1038/35017662. PMID 10894520. S2CID 205007392. Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- Cohen J (1994). "The Duesberg Phenomenon: A Berkeley virologist and his supporters continue to argue that HIV is not the cause of AIDS. A 3-month investigation by Science evaluates their claims" (PDF). Science. 266 (5191): 1642–1649. doi:10.1126/science.7992043. PMID 7992043.
- "Focus on the HIV-AIDS Connection: Resource links". National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Retrieved 2006-09-07.
- O'Brien SJ, Goedert JJ (1996). "HIV causes AIDS: Koch's postulates fulfilled". Curr. Opin. Immunol. 8 (5): 613–8. doi:10.1016/s0952-7915(96)80075-6. PMID 8902385.
- Galéa P, Chermann JC (1998). "HIV as the cause of AIDS and associated diseases". Genetica. 104 (2): 133–42. doi:10.1023/a:1003432603348. PMID 10220906. S2CID 10793378.
- ^ Smith TC, Novella SP (2007). "HIV denial in the Internet era". PLOS Med. 4 (8): e256. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0040256. PMC 1949841. PMID 17713982.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Chigwedere P, Seage GR, Gruskin S, Lee TH, Essex M (October 2008). "Estimating the Lost Benefits of Antiretroviral Drug Use in South Africa". Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes (1999). 49 (4): 410–415. doi:10.1097/QAI.0b013e31818a6cd5. PMID 18931626. S2CID 11458278.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|lay-url=ignored (help)CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Baleta A (2003). "S Africa's AIDS activists accuse government of murder". Lancet. 361 (9363): 1105. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12909-1. PMID 12672319. S2CID 43699468.
- ^ Blechner MJ (1997). Hope and mortality: psychodynamic approaches to AIDS and HIV. Hillsdale, NJ: Analytic Press. ISBN 0-88163-223-6.
