Triangular space
| Triangular space | |
|---|---|
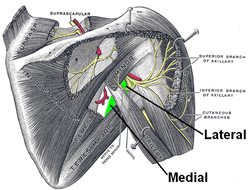 Suprascapular and axillary nerves of right side, seen from behind. The axillary spaces are labeled in green. Triangular space is the medial space. | |
 The scapular and circumflex arteries. (Triangular space is visible but not labeled.) | |
| Anatomical terminology |
The triangular space (also known as the medial triangular space,[1] upper triangular space,[2] medial axillary space or foramen omotricipitale[3]) is one of the three spaces found at the axillary space. The other two spaces are the quadrangular space and the triangular interval.[4]
Boundaries[edit]
It has the following boundaries:
- Inferior: the superior border of the teres major;
- Lateral: the long head of the triceps;
- Superior: Teres minor or Subscapularis
For the superior border, some sources list the teres minor,[2][5] while others list the subscapularis.[6]
Contents[edit]
It contains the scapular circumflex vessels.[7]
Unlike the quadrangular space or the triangular interval, no major nerve passes through the triangular space.

See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Photo at tufts.edu
- ^ a b Kyung Won, PhD. Chung (2005). Gross Anatomy (Board Review). Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 34. ISBN 0-7817-5309-0.
- ^ Valera Garrido, Fermin (October 2, 2015). Advanced Techniques in Musculoskeletal Medicine and Physiotherapy: Using Minimally Invasive Therapies in Practice. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 113. ISBN 9780702062346. Retrieved January 26, 2018.
- ^ Krishna, Garg (2010). "7 - Scapula". BD Chaurasia's Human Anatomy (Regional and Applied Dissection and Clinical) Volume 1 - Upper limb and thorax (Fifth ed.). India: CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd. pp. 81, 82. ISBN 978-81-239-1863-1.
- ^ Anatomy photo:03:05-0101 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Triangular Space of Scapular Region"
- ^ Adam Mitchell; Drake, Richard; Gray, Henry David; Wayne Vogl (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-06612-4.
- ^ Wasfi F, Ullah M (1985). "Structures passing through the triangular space of the human upper limb". Acta Anat (Basel). 123 (2): 112–3. doi:10.1159/000146049. PMID 4061026.
External links[edit]
- Diagram at microsurgeon.org
- Photo at tufts.edu
- Description at ganfyd.org
- Photo at ithaca.edu
 This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 445 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 445 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
