Order flow trading
Order flow trading is a type of trading strategy and form of analysis used by traders on the markets, other popular forms of market/trading analysis include technical analysis, sentiment analysis and fundamental analysis.[1]
Order flow trading is the process of analysing the flow of trades being placed by other traders on a specific market.[2] This is done by watching the Order Book and also footprint charts.[2] Order flow analysis allows traders to see what type of orders are being placed at a certain time in the market, e.g. the amount of Buy and Sell orders at a given price point.[3] Traders can use Order Flow analysis to see the subsequent impact on the price of the market by these orders and therefore make predictions on the future price and direction of the market. Order flow trading is a type of short term trading strategy as it is used to enter the market accurately based on recent executed buy and sell orders.[2] Order Flow Trading is sometimes referred to as a form of volume trading.[2]

Reading Footprint candles[edit]
The numbers on the left hand side of a footprint candle show the volume/amount of sell orders executed, the numbers on the right side of a footprint candle show the volume/amount of buy orders executed, footprint candles are read diagonally up, and to the right. E.g. a sell order on the left hand side is compared with a buy order one tick up, diagonally to the right of it.[4]

Order flow analysis generally shows the following[edit]
- Large buy or sell orders being executed
- who is in control, buyers or sellers
- volume
- VPOC: (volume point of control) the point at which the traded volume is the highest in the candle
- how big each buy or sell order is
- limit orders, available on DOM (depth of market) or order book.[2]
Order Flow analysis shows the volume of Buyers and Sellers at a specific price point and at a given time, it can also show the accumulation of orders waiting to be executed at different price levels. On candlestick charts this is shown more broadly by individual candlesticks, however, Order Books and footprint charts show the individual buy and sell orders placed within these candlesticks and therefore give a deeper view on the micro price movements. Order Flow traders can see both Limit orders and Market orders being placed, footprint charts show only executed market orders and therefore show the actual volume of buyers and sellers.[5] limit orders are price points where traders have ordered to buy or sell a stock, these orders will not get executed unless the price of the market hits their limit order price point.[6][7] These orders are not shown on candlesticks charts and can only be seen on Order Books, once these orders have been executed they turn to Market orders which are then displayed on the chart.[8]
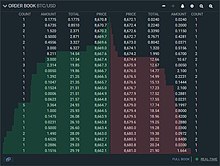
Order Flow Traders can see levels of support and resistance by the size of buy and sell orders. On a footprint chart these are shown by buy and sell imbalances.[4] A buy imbalance tells us that there are much more buyers than sellers at that price point, indicating potential support levels. A sell imbalance shows that there are a lot more sellers than buyers at that price point and this can indicate a potential resistance point.[9] The volume of buyers and sellers is also used to indicate potential trend reversals and is a strategy that some order flow traders will apply to footprint charts.[4]

Spoof Orders[edit]
Spoof orders or Spoofing are when traders will place orders at certain price points and then cancel these orders just before they are executed, they are used to deceive other trades into analysing false support and resistance levels.[10]
References[edit]
- ^ "3 Types of Forex Market Analysis". BabyPips.com. 2021-04-26. Retrieved 2021-12-17.
- ^ a b c d e Guides, Trading Strategy (2020-09-30). "Order Flow Trading Strategy".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Understanding Order Flow in the Forex Market". Forex Training Group. 2017-02-17. Retrieved 2021-12-17.
- ^ a b c "The Ultimate Guide To Profiting From Footprint Charts". Jumpstart Trading. 2019-08-21. Retrieved 2021-12-17.
- ^ Muñoz, Teresa Rocha. "Lesson 1 - The Basics of Order Flow & Volume Analysis". Jigsaw Trading. Retrieved 2021-12-17.
- ^ Schwab.com. "3 Order Types: Market, Limit and Stop Orders". Schwab Brokerage. Retrieved 2021-12-17.
- ^ "SEC.gov | Limit Orders". www.sec.gov. Retrieved 2021-12-17.
- ^ "Order Flow Analysis - The Secret Weapon of The Professional Traders". The5%ers | Funding Traders & Growth Program. 2021-01-06. Retrieved 2021-12-17.
- ^ "How to Identify Imbalance in the Markets with Order Flow Trading". Futures Day Trading Strategies. 2019-07-11. Retrieved 2021-12-17.
- ^ "Spoofing". Corporate Finance Institute. Retrieved 2021-12-17.
