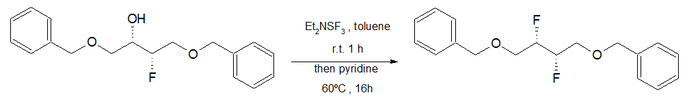
Olah reagent
The Olah reagent is a nucleophilic fluorinating agent. It consists of a mixture of 70% hydrogen fluoride and 30% pyridine; alcohols react with this reagent to give alkyl fluorides:

It acts as a stabilized, less volatile form of hydrogen fluoride. It is used in the fluorination of steroids and in deprotection of peptides.[1][2][3] Instead of hydrogen fluoride, several other fluorinating agents can be used, such as diethylaminosulfur trifluoride (DAST).