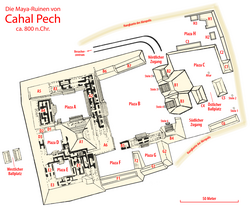
Cahal Pech
 | |
 | |
Location within Mesoamerica | |
| Location | San Ignacio, Cayo District, Belize |
|---|---|
| Region | Cayo District |
| History | |
| Founded | 1200 BCE |
| Abandoned | 900 CE |
| Periods | Classic |
| Cultures | Maya |
| Site notes | |
| Excavation dates | 1988 - 2000 |
| Archaeologists | Jaime Awe National Institute of Archaeology (NICH) |
| Architecture | |
| Architectural styles | Classic |
| Responsible body: Belize Department of Archaeology | |
Cahal Pech is a Maya site located near the town of San Ignacio in the Cayo District of Belize. The site was a palatial, hilltop home for an elite Maya family, and though the most major construction dates to the Classic period, evidence of continuous habitation has been dated to as far back as 1200 BCE during the Early Middle Formative period (Early Middle Preclassic), making Cahal Pech one of the oldest recognizably Maya sites in Western Belize.[1][2]
Location[edit]
The site rests high above the banks of the Macal River and is strategically located to overlook the confluence of the Macal River and the Mopan River. The site is a collection of 34 structures, with the tallest temple being about 25 meters in height, situated around a central acropolis. The site was abandoned in the 9th century CE for unknown reasons.[citation needed]
Archaeology[edit]
The earliest pottery in western Belize is found here.
"Emerging information from western Belize suggests that ceramic-using populations may have been in place as early as ca. 1200 B.C. at Cahal Pech and perhaps elsewhere (Awe 1992; Clark and Cheetham 2002; Garber et al. 2004; Healy and Awe 1995). While these complexes, termed "Cunil" at Cahal Pech and "Kanocha" at Blackman Eddy, remain to be broadly documented across the Belize River Valley, they are the earliest established ceramic technologies recorded in western Belize."[3]
The name Cahal Pech, meaning "Place of the Ticks" in the Yucatec Maya language,[4] was given when the area was used as pasture during the first archaeological studies in the 1950s, led by Linton Satterthwaite from the University of Pennsylvania Museum. It is now an archaeological reserve, and houses a small museum with artifacts from various ongoing excavations.
The primary excavation of the site began in 1988. Restoration was completed in 2000 under the leadership of Dr. Jaime Awe, Director of the National Institute of Archaeology (NICH), Belize.[5]
Other nearby Maya sites include Chaa Creek, Xunantunich, Baking Pot, and Lower Dover.
Gallery[edit]
-
Aerial of Cahal Pech
-
Main courtyard
-
Main courtyard
-
Main courtyard
-
Remains of a ball court
-
Another building
See also[edit]
Notes[edit]
References[edit]
- Awe, Jaime; Cassandra Bill; Mark Campbell; David Cheetham (1990). "Early Middle Formative Occupation in the Central Maya Lowlands: Recent Evidence from Cahal Pech, Belize" (PDF). Papers from the Institute of Archaeology. 1. London: UCL Institute of Archaeology: 1–5. ISSN 0965-9315. OCLC 231692266. Archived from the original (PDF online reproduction) on 2009-06-17. Retrieved 2008-08-05.
- Awe, Jaime (June 2000). "Cahal Pech". Archaeology Magazine.
- Awe, Jaime (2006). Maya Cities and Sacred Caves. Cubola Productions. ISBN 978-976-8161-10-9.
External links[edit]
 Media related to Cahal Pech at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Cahal Pech at Wikimedia Commons